DHCP Protocol
The hero who gives you an identity in the digital realm
Before we start with the engineering behind DHCP, here's what I want you to do. Assuming that you've kept your internet connection on, head over to settings-\>About your Phone-> Status info. You'll be able to see an option "IP address" in which below, there'll be two values. you've kept your internet connection on, now, turn off your internet connection, and check those values. Boom, they've vanished!! Where'd they go? Now if you will, turn on the internet connection and they're back again. Well, what sorcery is this? Fear not; we're about to unravel the magic behind this intriguing vanishing act.
What is DHCP?
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol [RFC - 2131] is an application-level network management protocol that automatically assigns IP addresses and other communication parameters to devices connected to a network. DHCP is a client-server protocol, with a DHCP server maintaining a pool of IP addresses that it can lease to DHCP clients. When a DHCP client (any electronic device that has a built-in DHCP client application) connects to a network, it sends a request to the DHCP server for an IP address. The DHCP server then assigns an IP address to the client from its pool of addresses. So, whenever you turned on the internet connection, your device asked for an IP address and the DHCP server provided you with one. And when you turn off the internet connection, your IP address will be taken back and recorded in the pool which can be used again for a new DHCP client.
DHCP allows a host to obtain an IP address automatically. A network administrator can configure DHCP such that the host receives the same IP address each time it connects to the network or a host may be assigned a temporary IP Address that will be different each time the host connects to the network.
DHCP is a Client-Server Protocol
DHCP is a Client-Server Protocol. A client is typically a newly arriving host wanting to obtain network configuration information, including and IP address for itself. In the simplest case, each subnet will have a DHCP server. If no server is present on the subnet, a DHCP Relay agent that knows the address of a DHCP server is needed.
DHCP Client-Server Interaction
For a newly arriving host, the DHCP protocol is a four step process:
From the following image, yiaddr is Your Internet Address.
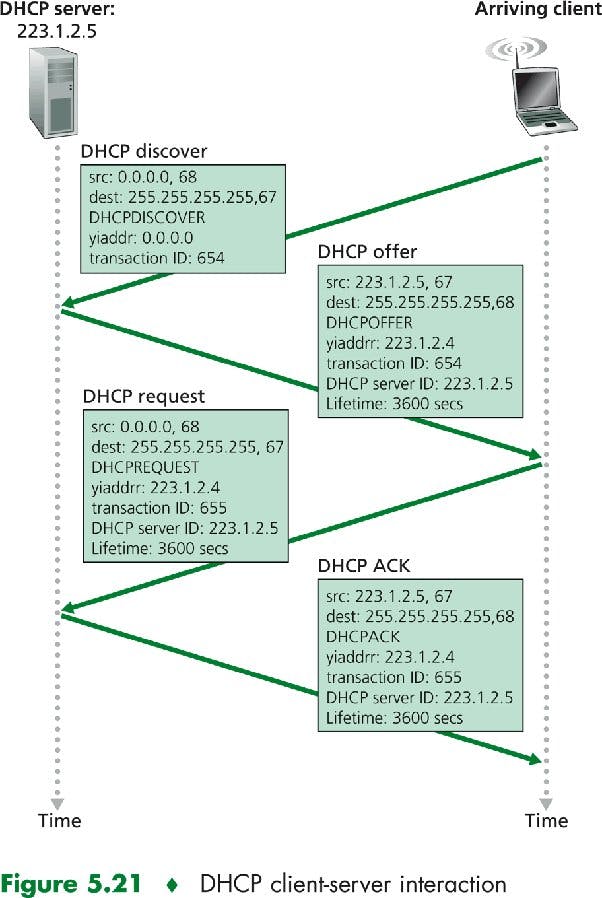
DHCP server discovery: The first task of a newly arriving host is to find a DHCP server. This is done by DHCP discover message, which a client sends within a UDP packet to port 67. The UDP packet is encapsulated in an IP datagram. Now, to whom should this be sent? The host doesn't even know anything about the network to which it is connecting, much less the address of the DHCP server. Given this, the DHCP client creates an IP datagram from the DHCP discover message along with a broadcast destination IP address of 255.255.255.255 and a "host" source IP address of 0.0.0.0. The DHCP client passes the IP datagram to the link layer, which then broadcasts this frame to all nodes in the subnet.
DHCP server offer(s): A DHCP server receiving a DHCP Discover Message responds to the client with a DHCP offer message that is broadcast to all nodes on the subnet, by using IP broadcast address of 255.255.255.255. If there are several DHCP servers in this subnet, the client may find itself with multiple offer messages. Each server offer message contains :
Transaction ID of received discover message
Proposed IP address for the client
Network mask
IP address lease time - the amount of time for which the IP address will be valid. [Mostly several hours or days]
DHCP request: The client will choose one offer and respond to its selected offer with a DHCP request message, echoing back the configuration parameters.
DHCP ack: The server responds to the DHCP request message with a DHCP ack message confirming the requested parameters.
Once the client receives the DHCP ack, the interaction is complete and the client can use the DHCP allocated address for the lease duration. The client can also renew its lease on an IP address.
Final Thoughts
The value of DHCP's plug-and-play capability is clear, considering the fact that the alternative is to manually configure a host's IP address. Consider moving from one point to another and joining a new subnet, thus obtaining a new IP address at each location. DHCP is the necessary and primary thing needed to connect to the Internet.